Speech Apraxia
Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) is a motor speech disorder that affects a child’s ability to verbally communicate. It affects the muscles used for speaking, making it harder for the child to control and coordinate the muscles to produce clear, understandable words. CAS can be quite confusing and overwhelming for both children and their families, so it is important to know what CAS is and the available options for treatment.
Get Treatment Now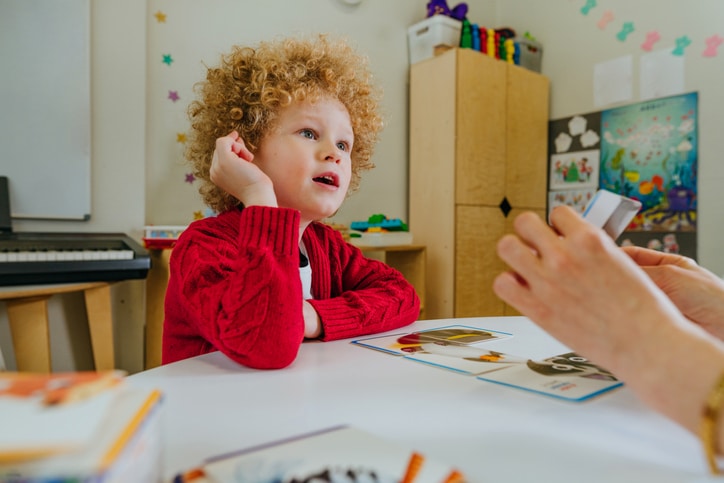
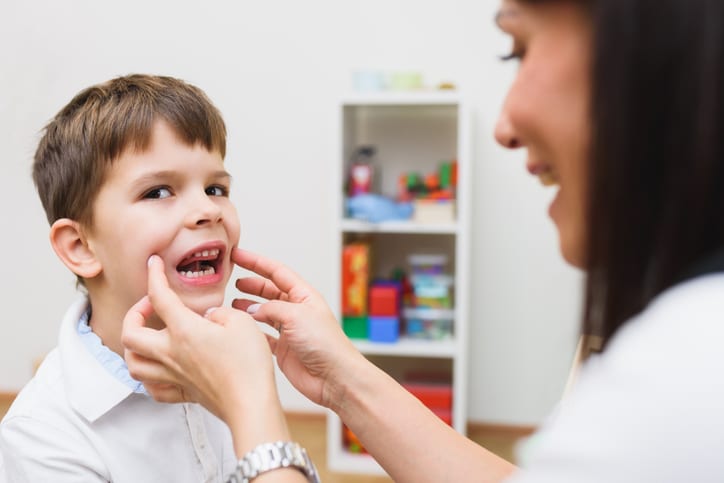
What is Apraxia of Speech in Children?
Childhood apraxia of speech is a motor speech disorder that can cause difficulty in producing sounds and putting them together to form words, phrases, or sentences. It occurs when the brain has difficulty sending messages to the muscles used for speaking. The child may know what they want to say but have trouble coordinating their mouth and tongue to say it. These challenges can impact the child’s social interactions and ability to learn.
What Causes Childhood Apraxia of Speech?
Although the exact cause of CAS remains unknown, it is thought to be related to damage within the brain nerve pathways responsible for speech. The damage can be caused by a variety of factors such as brain infection, genetic disorders, developmental disorders, or brain injury.
Assessing Childhood Apraxia of Speech
To accurately diagnose CAS, a speech pathologist will evaluate the child’s motor and language abilities. This evaluation will include observing the child’s ability to imitate sounds, as well as their understanding of spoken and written language. The speech pathologist may also use other assessments such as standardized tests to assess the severity of the child’s speech disorder.
Childhood Apraxia of Speech Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of CAS can vary depending on the individual. One of the key indicators of CAS is difficulty producing speech sounds accurately and in the correct order, even when given verbal cues or instruction. Other characteristics of childhood apraxia of speech may include a relatively long pause between words, difficulty producing sounds that make up words, and difficulty moving from one sound to the next.
Speech Therapy for Childhood Apraxia of Speech
For children with CAS, pediatric speech therapy is an important part of helping them to gain control over their speech muscles. Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) are specially trained to provide treatments that can help children learn how to articulate words and sentences more clearly, develop better motor control and coordination, and increase their ability to understand and use language.
Childhood Apraxia of Speech Therapy Techniques and Goals
When it comes to treating CAS, the main goal is to help the child improve their ability to produce speech sounds accurately and in the correct order. Speech-language pathologists use a variety of approaches to accomplish speech therapy goals, including:
- Targeted stimulation: providing targeted cues to help the child produce correct sounds or words, such as visual or tactile prompts
- Motor learning strategies: using strategies like imitation, repetition, and feedback to learn new skills
- Pragmatic strategies: learning how to use language in a social context
- Visual-gestural cues: using hand motions and facial expressions to aid speech
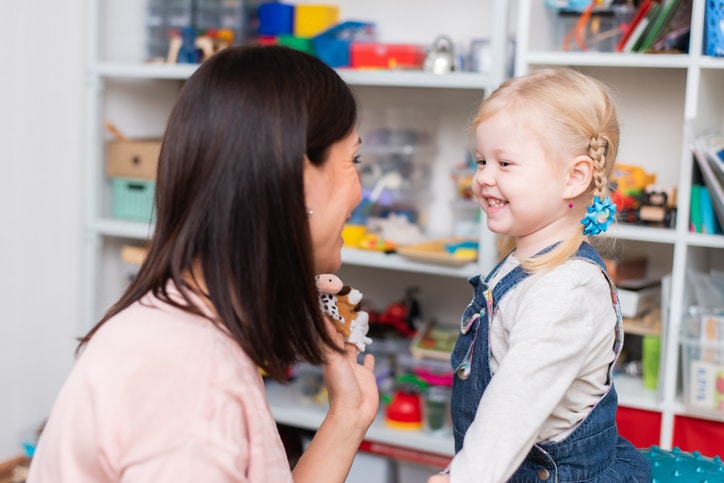

Childhood Apraxia Speech Therapy at Circle of Care
Through comprehensive assessments, research-based treatments, and individualized goals, our speech pathologists at Circle of Care strive to provide compassionate and effective therapy for children with CAS. Our goal is to help every child reach their full potential in communication and find their voice. Contact us today.
